Introduction
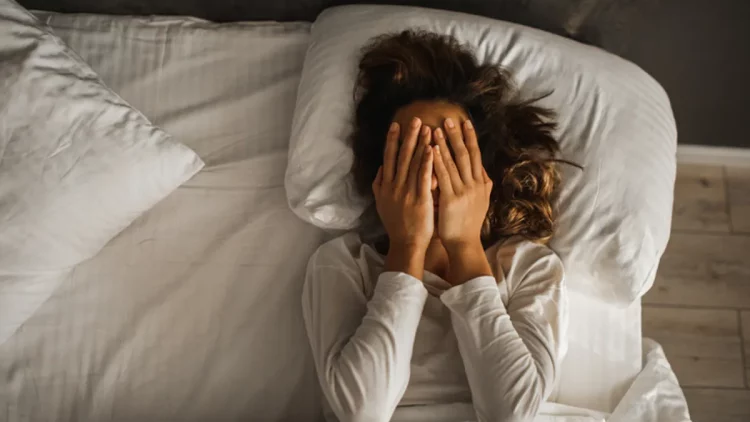
We’ve all heard it before: “Get enough sleep for healthy skin.” But, do you really know how sleep deprivation affects your body, especially your skin? It’s easy to brush off a night of poor sleep, thinking it won’t have much impact—but the truth is, chronic lack of sleep can harm your skin, body, and overall well-being in ways that are often more profound than we realize.
Sleep is a critical period for repair and rejuvenation in your body, including your skin. During deep sleep, your body is working to regenerate cells, repair tissues, and recover from the stresses of the day. Without sufficient rest, these processes are disrupted, leading to various skin concerns and physical health issues.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into how sleep deprivation affects your skin and body, and explore simple habits you can adopt to improve your sleep quality, allowing you to wake up with a refreshed complexion and a rejuvenated body. Let’s discover the connection between sleep and beauty—and how to reclaim your natural glow!
1. The Skin and Sleep Connection: Why Sleep Matters for Your Complexion
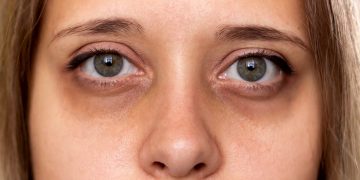
When you don’t get enough sleep, the first signs usually appear on your skin. From dark circles under your eyes to increased breakouts, the effects of poor sleep are highly visible. Let’s explore how a lack of sleep directly impacts your skin health:
Skin Regeneration is Compromised
Your skin goes into repair mode while you sleep, especially during deep sleep (also known as slow-wave sleep). This is when your body repairs damaged cells, produces collagen (the protein responsible for skin elasticity), and works to fix any environmental damage, such as UV exposure or pollution. When you’re not getting enough rest, this regeneration process is hindered, leading to skin that appears dull and aged.
Increased Inflammation
Lack of sleep triggers the body’s stress response, which increases the production of the stress hormone cortisol. Elevated cortisol levels can increase inflammation in the skin, contributing to breakouts, redness, and even conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Inflammation also slows down the healing process, meaning that pimples or skin irritations take longer to recover.
Dehydrated Skin
Sleep deprivation can reduce the skin’s ability to retain moisture. Dry, flaky skin is a common symptom of not getting enough sleep. Your skin may also look puffy or inflamed, especially around the eyes, due to poor circulation and fluid retention. This leads to fine lines and a lackluster appearance.
Premature Aging
Chronic sleep deprivation leads to a decrease in the production of growth hormone, which is responsible for skin repair. Reduced growth hormone levels result in weakened skin elasticity, and over time, this can contribute to wrinkles and sagging. Additionally, oxidative stress—caused by lack of sleep—can lead to premature aging by damaging skin cells, further exacerbating the appearance of fine lines.
2. The Impact of Sleep on Your Body: Why You Need Rest for Optimal Health
While sleep has an obvious effect on your skin, its impact on the entire body is equally important. Poor sleep not only makes you look tired, but it also diminishes your body’s overall health and performance. Let’s explore the key areas that suffer due to lack of sleep:
Immune System Function
Sleep is essential for a strong immune system. When you don’t sleep enough, your body’s ability to fight off infections decreases. Studies have shown that people who don’t get enough rest are more susceptible to colds and other illnesses. This can lead to prolonged recovery times, meaning you’re not only feeling sluggish but also compromising your overall well-being.
Hormonal Imbalance
Sleep deprivation affects the balance of several important hormones in your body. For instance, it can increase the production of ghrelin, the hormone responsible for hunger, while reducing levels of leptin, the hormone that makes you feel full. This leads to increased cravings, especially for high-sugar and high-fat foods, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight and promoting an unhealthy cycle of overeating.
Lack of sleep also impacts the production of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. This can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes over time.
Mental Health and Stress Levels
Poor sleep is strongly linked to an increase in anxiety and depression. When you don’t sleep enough, your brain’s ability to manage stress and regulate emotions is diminished. This can lead to irritability, mood swings, and increased feelings of overwhelm. On top of that, sleep deprivation reduces your ability to focus, make decisions, and solve problems efficiently, affecting your overall productivity.
Muscle Recovery and Performance
Sleep is the body’s natural recovery tool, especially after exercise. Without adequate rest, muscles don’t have enough time to repair and rebuild. This leads to decreased strength, slower recovery times, and a greater risk of injury. For those engaging in intense workouts or athletic training, poor sleep can seriously affect performance and stamina.
3. The Hidden Dangers: How Sleep Deprivation Contributes to Long-Term Health Issues
While you may notice some immediate effects of poor sleep (like feeling sluggish or dealing with more breakouts), the long-term consequences can be even more serious. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to several major health conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Sleep plays a vital role in heart health. A lack of sleep increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. It can also lead to an increase in inflammation in the arteries, contributing to atherosclerosis (plaque build-up in the arteries).
- Weight Gain: Studies have shown that people who consistently get less than 7 hours of sleep per night tend to have a higher body mass index (BMI). This is partly due to hormonal imbalances (increased ghrelin and decreased leptin), which can lead to increased fat storage.
- Decreased Life Expectancy: Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to a shorter lifespan. According to studies, people who sleep less than 6 hours per night on a regular basis may have an increased risk of dying prematurely from various causes, including cancer and heart disease.

4. Habits to Improve Sleep Quality: Reclaim Your Glow and Health
Now that we understand how sleep deprivation affects both skin and body, let’s explore some practical sleep habits you can implement to improve your quality of rest and overall health:
1. Stick to a Sleep Schedule
Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night to give your body ample time to recover.
2. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Your sleep environment plays a huge role in the quality of your rest. Make your bedroom as comfortable as possible by:
- Keeping it dark—use blackout curtains to block out light.
- Reducing noise—consider using earplugs or a white noise machine.
- Adjusting temperature—keep the room slightly cool for better sleep.
- Keeping electronics like phones and computers out of the room to avoid distractions.
3. Watch What You Eat Before Bed
Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bed, as these can interfere with your sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can stay in your system for hours, and alcohol can disrupt your sleep cycle, making it harder for you to enter the deeper stages of rest.
4. Practice Relaxation Techniques
To wind down before bed, consider incorporating relaxation techniques like:
- Deep breathing exercises or meditation.
- Gentle yoga or stretching.
- Reading a book or listening to calming music.
5. Limit Screen Time
The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with melatonin production, a hormone that regulates sleep. Turn off electronic devices like phones, tablets, and computers at least 30 minutes to an hour before bed.
6. Get Active During the Day
Engaging in regular physical activity during the day can promote better sleep at night. However, try not to exercise too close to bedtime, as this can have the opposite effect and leave you feeling too energized to sleep.
Conclusion
Sleep deprivation is not just a temporary inconvenience—it can have long-lasting effects on your skin, body, and overall health. From increased inflammation to accelerated aging and reduced immune function, poor sleep impacts virtually every aspect of your well-being. But the good news is that improving your sleep habits doesn’t have to be complicated.
By adopting simple changes like sticking to a sleep schedule, creating a peaceful sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques, you can greatly improve your sleep quality and, in turn, your health and beauty. When you allow your body the rest it needs, you’ll wake up feeling refreshed and glowing—inside and out.
Start today, and give your skin and body the nourishment and recovery they deserve through quality sleep!