When it comes to skin health, many people focus primarily on topical products, such as lotions, serums, and creams. While skincare routines certainly play a vital role in maintaining healthy skin, the foundation of glowing, radiant skin actually begins from within. One of the most powerful tools for promoting skin health and achieving that coveted inner glow is through a balanced, nutrient-rich diet.
Our skin is the body’s largest organ, and it reflects the choices we make regarding our diet, lifestyle, and overall health. Nutrients obtained from food directly impact the health of our skin, influencing hydration, elasticity, and even the speed at which we age. By understanding the connection between what we eat and the condition of our skin, we can make informed decisions to nourish our skin from the inside out.
In this article, we will explore how a balanced diet contributes to skin health and the foods that can help you achieve radiant, youthful-looking skin. From antioxidants to healthy fats and essential vitamins, we’ll break down the nutrients essential for glowing skin and provide tips on incorporating these into your daily meals.
1. The Role of Nutrition in Skin Health
Our skin requires a variety of nutrients to function properly. A well-balanced diet can help keep the skin hydrated, support collagen production, reduce inflammation, and protect against environmental damage. Certain nutrients play a pivotal role in maintaining the skin’s structure, while others are involved in the repair and regeneration processes.
A. Skin’s Structure and Function
The skin is composed of multiple layers, and its outermost layer, known as the epidermis, acts as a barrier to protect against harmful environmental factors such as UV rays, pollutants, and bacteria. Beneath the epidermis, the dermis contains collagen and elastin, proteins that provide the skin with structure, strength, and elasticity. Proper nutrition ensures the skin has the building blocks it needs to maintain these proteins and repair any damage that occurs.
B. Importance of Hydration
Hydrated skin is key to achieving a healthy, radiant complexion. Dehydration can lead to dry, flaky, and dull skin, while adequate hydration keeps the skin smooth and plump. Water is essential for the transportation of nutrients to the skin cells, so drinking enough fluids is just as important as consuming nutrient-dense foods.
2. Key Nutrients for Healthy Skin
A balanced diet that includes a wide variety of foods can provide the essential nutrients needed for optimal skin health. Below are some key nutrients that play a significant role in nourishing the skin:
A. Antioxidants: Protecting the Skin from Free Radical Damage
Antioxidants are compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage skin cells and accelerate the aging process, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging. A diet rich in antioxidants can help protect the skin from oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, and promote a youthful complexion.
- Vitamin C: One of the most powerful antioxidants, vitamin C is essential for collagen production and skin repair. It also helps protect the skin from UV damage and brightens the complexion. Rich sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- Vitamin E: Another potent antioxidant, vitamin E helps protect the skin from environmental damage and promotes healing. It also plays a role in preventing dryness and maintaining skin elasticity. Good sources of vitamin E include nuts, seeds, spinach, and avocados.
- Beta-Carotene: A form of vitamin A, beta-carotene is found in orange and yellow vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, and pumpkin. It supports the skin’s natural barrier function and helps protect it from sun damage.
B. Healthy Fats: Maintaining Skin Elasticity and Hydration
Healthy fats are essential for maintaining the skin’s moisture levels and elasticity. These fats help nourish the skin from within, keeping it smooth, hydrated, and supple.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s are essential fats that help reduce inflammation, protect against UV damage, and maintain the skin’s moisture barrier. Foods rich in omega-3s include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Monounsaturated Fats: These fats help lock in moisture and prevent dryness. Olive oil, avocados, and nuts are excellent sources of monounsaturated fats that support healthy skin.
C. Proteins: Building Blocks for Skin Repair and Regeneration
Collagen, the protein responsible for skin’s strength and elasticity, naturally decreases with age. Protein-rich foods support collagen production, repair damaged skin, and promote healthy cell turnover.
- Collagen-Boosting Foods: Bone broth, chicken skin, and fish are rich in collagen and amino acids, which help repair damaged skin tissue and stimulate collagen production. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and peppers, also support collagen synthesis.
- Plant-Based Proteins: For those on a plant-based diet, protein-rich options such as beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa provide the necessary building blocks for skin repair.
D. Vitamins and Minerals: Supporting Skin Health and Repair
In addition to antioxidants and healthy fats, vitamins and minerals are crucial for skin health. These nutrients support the skin’s natural functions and promote regeneration.
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A is essential for skin cell turnover and repair. It helps prevent dry, flaky skin and promotes a youthful, glowing complexion. Sources of vitamin A include sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach, and kale.
- Zinc: Zinc plays a key role in skin healing and can help regulate oil production. It also helps protect the skin from acne and inflammation. Foods high in zinc include oysters, pumpkin seeds, cashews, and chickpeas.
- Biotin: Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, supports healthy skin, hair, and nails. A deficiency in biotin can lead to skin rashes and dryness. Good sources of biotin include eggs, almonds, spinach, and sweet potatoes.
3. The Impact of Hydration on Skin Health
Hydration is one of the most important factors for maintaining healthy skin. Our skin needs moisture to stay plump and radiant, and dehydration can lead to dryness, dullness, and fine lines. While drinking water is essential for hydration, it is also important to consume hydrating foods that provide moisture to the skin.
A. The Role of Water in Skin Hydration
Water helps deliver nutrients to the skin and flushes out toxins. When the body is well-hydrated, the skin appears smooth, dewy, and youthful. Conversely, dehydration can result in dry, flaky skin and the appearance of fine lines.
- Aim to drink at least 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water a day, but this may vary depending on activity levels, climate, and individual needs.
- Include water-rich foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, oranges, and leafy greens in your diet to help maintain hydration levels.
B. Hydrating Foods for Glowing Skin
Certain foods not only provide hydration but also help lock in moisture. Some hydrating foods to incorporate into your diet include:
- Cucumbers: High in water content, cucumbers help keep the skin hydrated and reduce puffiness.
- Berries: Rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, berries hydrate the skin while helping to protect against oxidative damage.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that protects the skin from sun damage and supports collagen production.
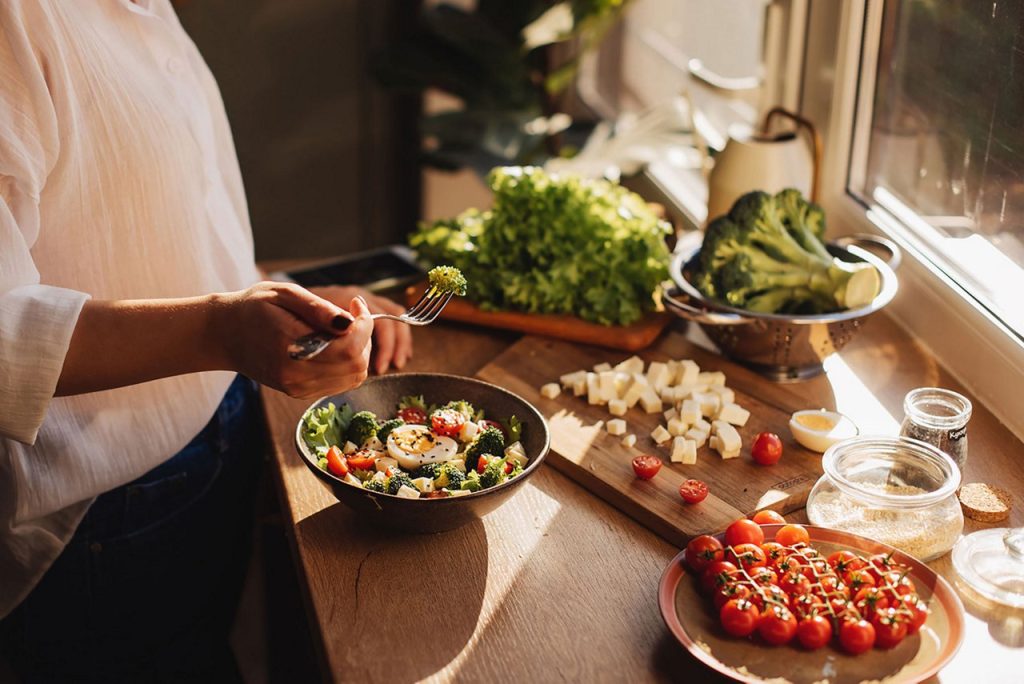

4. Foods to Avoid for Optimal Skin Health
Just as certain foods can promote healthy skin, others can have a negative impact on your complexion. Certain dietary habits can trigger inflammation, acne, and other skin concerns.
A. Refined Sugars and Carbohydrates
A diet high in refined sugars and carbohydrates can lead to an increase in insulin levels, which in turn triggers inflammation and the production of oil. This can exacerbate conditions such as acne and lead to skin aging. Avoiding sugary snacks, sodas, and processed foods can help keep your skin clear and youthful.
B. Dairy Products
Some studies suggest that dairy products, especially milk, may contribute to acne flare-ups in some individuals. If you notice that your skin reacts negatively to dairy, consider reducing your intake or opting for plant-based alternatives.
C. Excessive Alcohol and Caffeine
Excessive alcohol consumption can dehydrate the skin, leading to dryness and dullness. Caffeine can also have a dehydrating effect on the skin. Moderating your intake of alcohol and caffeine can help maintain your skin’s hydration levels.
5. Creating a Skin-Healthy Meal Plan
Incorporating skin-boosting foods into your diet doesn’t have to be difficult. Here’s an example of a skin-friendly meal plan for one day that includes nutrient-dense foods:
Breakfast:
- Avocado toast with whole-grain bread and a sprinkle of chia seeds
- A smoothie made with spinach, frozen berries, almond milk, and a scoop of plant-based protein powder
Lunch:
- Quinoa salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, chickpeas, cucumber, and olive oil dressing
- A side of fresh fruit, such as oranges or strawberries
Snack:
- A handful of almonds and walnuts
Dinner:
- Grilled salmon with a side of steamed broccoli, sweet potatoes, and a mixed salad
- A glass of water or herbal tea
6. Conclusion: Nourishing Your Skin from the Inside Out
Achieving glowing, youthful skin requires more than just a good skincare routine. By adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, you can support your skin’s health from the inside out. From antioxidants and healthy fats to vitamins, minerals, and hydration, the foods you eat play a significant role in maintaining the appearance and function of your skin. By nourishing your skin through diet, you can promote a glowing complexion and reduce the risk of common skin concerns like acne, wrinkles, and dryness. Embrace a skin-friendly diet today, and watch your skin radiate from within!