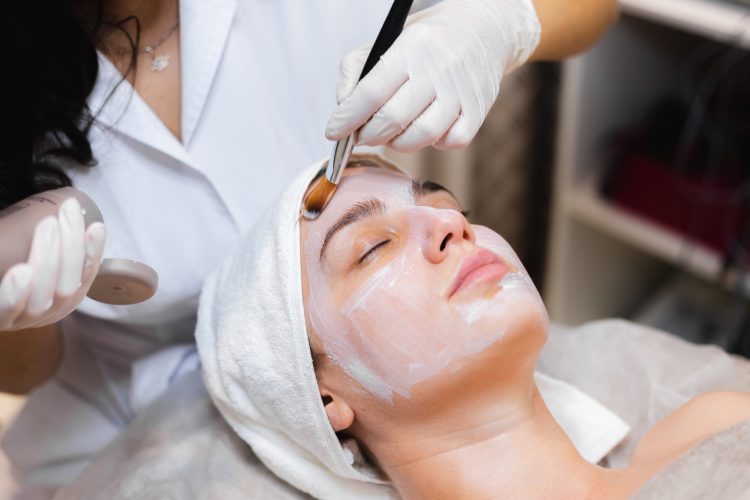
Chemical peels have long been a popular and effective method for improving the appearance and texture of the skin. This non-surgical treatment involves applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes it to exfoliate and eventually peel off, revealing fresh, youthful skin underneath. But despite their popularity, one of the main concerns many people have about chemical peels is the risk of scarring. In this article, we will delve into what chemical peels are, the different types available, the skin concerns they can address, the procedure and aftercare process, as well as the risks involved, including the possibility of scarring. Ultimately, we will explore whether chemical peels are a safe option for transforming your skin without leaving lasting damage.
Introduction: What Are Chemical Peels?
A chemical peel is a cosmetic treatment that uses a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin. By applying the solution to the skin’s surface, it causes the outer layers to shed, revealing healthier, smoother skin beneath. The treatment is typically used to address a variety of skin concerns, such as fine lines, acne scars, uneven skin tone, and hyperpigmentation. Chemical peels are available in different strengths, and their effects can range from mild exfoliation to deep rejuvenation, depending on the type of peel used.
The procedure is most commonly performed on the face, but it can also be done on the neck, chest, hands, and other areas where skin texture and tone need improvement. Chemical peels are a non-invasive way to improve the overall appearance of the skin, offering results that can help individuals achieve smoother, more youthful-looking skin without undergoing surgery. However, the type of chemical peel chosen will determine the results and potential risks.
Types of Peels: Light, Medium, and Deep Peels
Chemical peels come in three primary categories: light, medium, and deep peels. Each of these types is designed to address specific skin concerns and deliver different levels of exfoliation. Understanding these three types will help determine which peel is right for your skin and concerns.
- Light Peels:
Light peels, also known as superficial peels, are the mildest type of chemical peel. They typically use alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), such as glycolic acid or salicylic acid. These peels only affect the outermost layer of skin (the epidermis) and are used to treat superficial skin issues like mild acne, fine lines, and uneven skin tone.
Light peels are ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or those looking for a subtle improvement in skin texture. They typically require no downtime, and the recovery process is minimal. The results are often temporary, and repeated treatments may be necessary to maintain the improvements.
- Medium Peels:
Medium peels are more intense and penetrate deeper into the skin compared to light peels. They use stronger chemical solutions, such as trichloroacetic acid (TCA) or a combination of AHAs and BHAs, to treat a wider range of skin issues, including more severe acne, moderate wrinkles, and some forms of hyperpigmentation. Medium peels are designed to remove the outer and middle layers of skin, promoting the growth of new, healthier skin.
These peels require some downtime, as the skin will typically be red and may scab or peel over several days following the treatment. The results are more noticeable and longer-lasting than those of light peels, and many patients report improved skin texture, reduced pigmentation, and the appearance of smoother skin after just one treatment. However, repeated treatments may still be needed for optimal results.
- Deep Peels:
Deep peels are the most intense type of chemical peel and are used to treat more significant skin concerns, such as deep wrinkles, severe acne scars, and extensive sun damage. The chemical solution used in deep peels, usually phenol, penetrates deeply into the skin, removing the outer layers and stimulating collagen production. This type of peel can significantly improve the skin’s texture and tone, providing more dramatic and long-lasting results.
Deep peels typically require more downtime, with the skin taking several weeks to heal. Redness, scabbing, and peeling are common, and patients may need to take time off work or avoid public outings during the recovery process. Deep peels also carry a higher risk of side effects, including scarring, so they should only be performed by an experienced dermatologist or cosmetic surgeon.
Skin Concerns Addressed: Acne Scars, Hyperpigmentation, Wrinkles
Chemical peels can address a variety of skin concerns, making them a versatile treatment option for individuals looking to improve their complexion. Here are some of the primary skin issues that chemical peels are used to treat:
- Acne Scars:
Acne scars are one of the most common reasons people turn to chemical peels. Whether they are caused by cystic acne or more superficial blemishes, acne scars can make the skin appear uneven and textured. Chemical peels, particularly medium and deep peels, are effective at reducing the appearance of acne scars by exfoliating the damaged skin and stimulating collagen production. As new, healthier skin forms, the scars fade, and the skin becomes smoother.
- Hyperpigmentation:
Hyperpigmentation refers to dark spots or patches of skin that are caused by an overproduction of melanin. This can be due to sun damage, aging, pregnancy, or certain medications. Chemical peels, especially light and medium peels, can help even out skin tone by removing the outer layers of pigmented skin cells. Over time, the treated areas will lighten, and the skin will appear more radiant and even.
- Wrinkles and Fine Lines:
As we age, the skin loses collagen and elasticity, leading to the development of fine lines and wrinkles. Chemical peels can help reduce the appearance of these signs of aging by stimulating collagen production and promoting the growth of new skin cells. Light and medium peels are particularly effective for treating fine lines, while deeper peels can address more significant wrinkles and sun damage.

Procedure and Aftercare: What to Expect During and After Treatment
The chemical peel procedure typically follows a similar process, regardless of the type of peel being used. Here’s a breakdown of what to expect before, during, and after the treatment:
- Before the Peel:
Before undergoing a chemical peel, a consultation with a licensed professional is essential. The provider will assess your skin type, discuss your concerns, and recommend the most suitable type of peel for your needs. You may be asked to avoid certain skincare products, such as retinoids or exfoliants, for a period before the procedure to minimize irritation.
- During the Peel:
The procedure itself typically takes anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the type of peel and the size of the treatment area. During the procedure, the chemical solution is applied to the skin using a brush or cotton swab. You may experience a tingling or burning sensation as the solution is applied, but this discomfort usually subsides after a few minutes. For deeper peels, local anesthesia may be applied to minimize discomfort.
- After the Peel:
After the procedure, the skin may be red, swollen, and sensitive. The extent of recovery time depends on the type of peel. For light peels, there is typically no downtime, and the skin will begin to peel or flake off after a few days. Medium peels may cause more noticeable peeling, which can last for several days to a week, while deep peels may require several weeks of recovery.
To ensure proper healing and minimize complications, aftercare is crucial. You will be advised to avoid sun exposure, use gentle skincare products, and apply moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated. You may also need to avoid strenuous activities or anything that could irritate the skin during the recovery period.
Risks: Over-Peeling and Scarring Potential
While chemical peels are generally safe, they do carry some risks, especially if not performed correctly. The main risks associated with chemical peels include:
- Over-Peeling:
Over-peeling occurs when too many layers of skin are removed during the procedure, leading to excessive dryness, irritation, and even scarring. This is more common with medium and deep peels, particularly if the procedure is done too aggressively. It is essential to have the treatment performed by a qualified professional to avoid over-peeling.
- Scarring:
Scarring is a rare but possible complication of chemical peels. Deep peels, in particular, carry a higher risk of scarring, especially if the skin is not properly cared for during the healing process. The risk of scarring can also increase if the patient has a history of keloid scarring or if the peel is performed improperly.
- Hyperpigmentation or Hypopigmentation:
In some cases, chemical peels can cause the skin to become either lighter (hypopigmentation) or darker (hyperpigmentation) than before the treatment. This is more common in individuals with darker skin tones and is typically a temporary condition. However, in some cases, it can be permanent.
Conclusion: Are Chemical Peels Safe for Everyone?
Chemical peels are a highly effective treatment for improving skin texture, tone, and overall appearance. They can address a wide range of skin concerns, including acne scars, hyperpigmentation, and wrinkles. However, the safety of chemical peels depends on the type of peel, the experience of the practitioner, and the patient’s skin type and condition.
While the risk of scarring and other complications is minimal when performed by a trained professional, it is important to follow aftercare instructions and avoid over-exfoliating the skin. Chemical peels are generally safe for most individuals, but those with sensitive skin, darker skin tones, or certain medical conditions should consult with a dermatologist to ensure that the procedure is appropriate for their skin type.
Ultimately, if you’re considering a chemical peel to transform your skin, it’s essential to consult with a licensed provider to determine the best course of action and ensure that the procedure is performed safely.