In the evolving world of aesthetic medicine, dermal fillers have become one of the most popular non-surgical treatments for facial rejuvenation. Whether it’s restoring lost volume, smoothing wrinkles, or enhancing facial contours, dermal fillers offer versatile solutions for a youthful appearance. But with a variety of fillers available, different application techniques, and essential safety considerations, understanding how they work is crucial before undergoing treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the types of dermal fillers, their applications, safety measures, pre- and post-care tips, and how to choose a qualified practitioner.
Types of Dermal Fillers
Dermal fillers are injectable substances designed to restore volume, fill wrinkles, and improve facial contours. The main types commonly used in aesthetic practice include hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers, calcium-based fillers, and poly-L-lactic acid fillers.
1. Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Fillers
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the skin that attracts and retains water, keeping the skin hydrated and plump. HA fillers are the most widely used due to their safety, versatility, and reversibility.
- Properties: Smooth, gel-like consistency that integrates well into the skin
- Applications:
- Nasolabial folds (smile lines)
- Lips (volume and shape enhancement)
- Cheeks (volume restoration)
- Tear troughs under the eyes
- Duration: Typically lasts 6–18 months depending on the product and treatment area
- Reversibility: HA fillers can be dissolved using hyaluronidase in case of overcorrection or complications
2. Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA) Fillers
Calcium-based fillers are composed of tiny calcium microspheres suspended in a gel carrier. These fillers not only provide immediate volume but also stimulate natural collagen production.
- Properties: Thicker and firmer than HA, ideal for deeper facial lines and structural support
- Applications:
- Cheek augmentation
- Jawline contouring
- Chin enhancement
- Nasolabial folds (for deeper wrinkles)
- Duration: Typically lasts 12–18 months
- Note: These fillers are not reversible like HA, so precision in placement is crucial
3. Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) Fillers
Poly-L-lactic acid fillers are biostimulatory fillers that work gradually by encouraging collagen production rather than providing immediate volume.
- Properties: Powder or microparticles reconstituted before injection
- Applications:
- Facial volume loss
- Deep wrinkles
- Structural support for cheeks or temples
- Duration: Results appear gradually over several months and can last up to 2 years
- Note: Multiple sessions are often required to achieve optimal results
Applications and Targeted Areas
Dermal fillers can address various cosmetic concerns, from wrinkle reduction to facial sculpting. Common areas and applications include:
- Lips – Enhancement of shape, definition, and volume. Popular treatments include lip augmentation and correcting asymmetry.
- Cheeks – Restoration of volume lost due to aging, enhancing midface projection.
- Nasolabial Folds – Softening deep lines that run from the nose to the mouth corners.
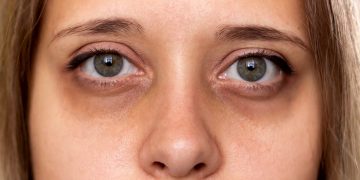
- Tear Troughs – Reducing the appearance of under-eye hollows and dark circles.
- Jawline and Chin – Contouring and definition for a more balanced profile.
- Hands – Rejuvenating volume loss in aging hands for smoother appearance.
- Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty – Correcting minor asymmetries or lifting the nasal tip without surgery.
Each filler type has ideal areas of application. HA fillers are versatile and suitable for most facial areas, while CaHA is preferred for deeper structural support. PLLA works best for gradual volumization and overall facial rejuvenation.
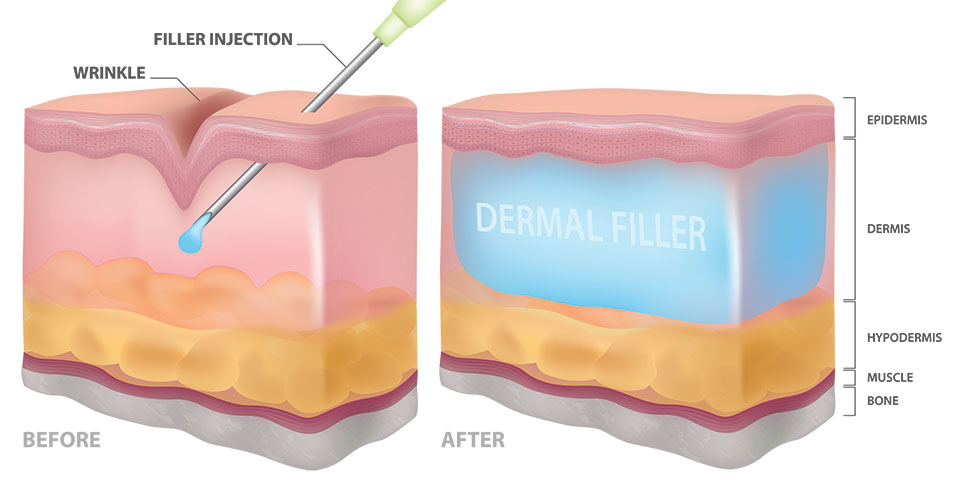
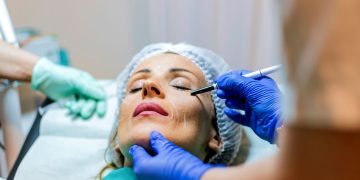
Safety and Side Effects
While dermal fillers are generally safe when administered by qualified practitioners, understanding potential side effects and risks is essential:
Common Side Effects
- Redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site
- Mild tenderness or discomfort
- Temporary lumps or bumps, often resolving within days
Rare but Serious Risks
- Infection at the injection site
- Allergic reactions
- Vascular complications (e.g., inadvertent injection into a blood vessel)
- Skin necrosis (rare, usually due to improper technique)
Mitigating risks involves proper patient assessment, careful injection technique, and immediate recognition and management of complications. Using sterile equipment and adhering to safety protocols are critical for successful outcomes.
Pre- and Post-Care
Proper pre- and post-treatment care enhances results and minimizes side effects.
Pre-Treatment Tips
- Avoid blood-thinning medications, supplements, or alcohol for several days prior, unless prescribed by a doctor
- Discuss any medical conditions, allergies, or previous cosmetic procedures with your practitioner
- Hydrate adequately and maintain healthy skin
Post-Treatment Care
- Avoid strenuous exercise, saunas, or hot baths for 24–48 hours
- Apply cold compresses to reduce swelling or bruising
- Avoid massaging or pressing the treated area unless instructed
- Follow-up appointments may be needed to assess results and touch-ups
Adhering to these guidelines helps achieve optimal results while reducing complications.
Choosing a Qualified Practitioner
Selecting a skilled and experienced practitioner is one of the most important factors for safe and effective dermal filler treatments. Consider the following:
- Credentials and Training – Ensure the practitioner is certified in aesthetic medicine or dermatology and trained in filler injection techniques.
- Experience – Ask about their experience with the specific type of filler and procedure you are seeking.
- Before-and-After Portfolio – Reviewing previous patient outcomes provides insight into their skill and aesthetic judgment.
- Consultation – A thorough consultation should include assessment of facial anatomy, discussion of realistic goals, and explanation of risks and benefits.
- Clinic Standards – Confirm that the clinic follows strict hygiene protocols, uses FDA-approved products, and has emergency procedures in place.
A qualified practitioner not only ensures safety but also tailors treatments to achieve natural, balanced results.
Conclusion
Dermal fillers have revolutionized non-surgical facial rejuvenation, offering versatile solutions for volume restoration, wrinkle reduction, and facial contouring. Understanding the differences between hyaluronic acid, calcium-based, and poly-L-lactic acid fillers helps in selecting the right treatment for your goals. Applications span lips, cheeks, jawlines, tear troughs, and even hands, with results ranging from immediate to gradual improvements. While side effects are generally mild, safety is paramount, and choosing a qualified practitioner is essential for a successful and natural-looking outcome. By following proper pre- and post-care instructions, patients can enjoy safe, effective, and long-lasting facial enhancements.