Healthy, radiant skin is often considered a reflection of overall wellness, and one of the most critical yet overlooked factors in skin health is sleep. While diet, skincare products, and sun protection are widely emphasized, the restorative power of sleep plays a central role in maintaining skin’s elasticity, hydration, and overall appearance. Chronic sleep deprivation can accelerate aging, impair the skin barrier, and exacerbate conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. This comprehensive guide explores how sleep affects skin health, the consequences of insufficient rest, tips for optimal sleep hygiene, and nighttime routines that promote glowing skin.
How Sleep Affects Collagen and Elasticity
Sleep is a period of profound physiological restoration, during which the body undertakes crucial repair processes, including those related to the skin.
- Collagen Production:
Collagen, a structural protein responsible for skin firmness and elasticity, is actively produced during deep sleep stages. Growth hormone, released predominantly during slow-wave sleep, stimulates collagen synthesis. Adequate sleep allows the skin to maintain its elasticity and resilience, while chronic sleep deprivation reduces collagen levels, leading to premature sagging and wrinkle formation. - Skin Barrier Function:
The skin barrier protects against environmental toxins, pollutants, and pathogens. During sleep, the skin replenishes lipids and strengthens this barrier. Poor sleep weakens barrier function, making the skin more prone to irritation, dryness, and sensitivity. - Repair of Cellular Damage:
Daytime exposure to UV rays, pollution, and oxidative stress causes cellular damage. At night, the body increases blood flow to the skin, delivering oxygen and nutrients that support cellular repair. Adequate sleep enhances the skin’s ability to recover from environmental stressors. - Regulation of Skin Hydration:
Sleep affects water balance and moisture retention in the skin. Lack of sleep can impair hydration, resulting in dull, dehydrated, and fatigued-looking skin.
Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
Insufficient or poor-quality sleep has several visible and long-term effects on skin health.
- Premature Aging:
Chronic sleep deprivation accelerates the breakdown of collagen and elastin, contributing to fine lines, wrinkles, and loss of skin elasticity. - Dark Circles and Puffiness:
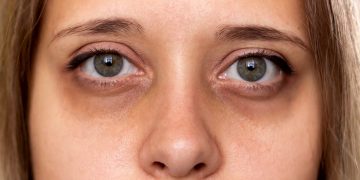
Reduced blood circulation and fluid accumulation around the eyes during inadequate sleep cause dark circles, under-eye bags, and puffiness. - Dull Complexion:
Impaired blood flow and reduced cell turnover result in a sallow, uneven, or tired-looking complexion. - Exacerbation of Skin Conditions:
Sleep deprivation can worsen inflammatory skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis due to increased cortisol levels and impaired immune response. - Delayed Healing:
Sleep is crucial for wound healing and recovery from skin injuries or procedures. Poor sleep slows the skin’s regenerative processes, prolonging healing time.

Sleep Hygiene Tips for Healthy Skin
Maintaining good sleep hygiene is essential for maximizing the restorative benefits of rest for the skin. Key strategies include:
- Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate the body’s circadian rhythm. - Create a Restful Environment:
Ensure the bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Consider blackout curtains, white noise machines, or fans to create an ideal sleep environment. - Limit Screen Time Before Bed:
Blue light emitted from phones, tablets, and computers can suppress melatonin production, delaying sleep onset. Aim to reduce screen exposure at least 1 hour before bedtime. - Avoid Stimulants:
Caffeine, nicotine, and other stimulants can interfere with sleep quality. Avoid these substances in the hours leading up to bedtime. - Relaxation Techniques:
Incorporate calming activities such as reading, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or gentle yoga to signal the body it’s time to sleep. - Regular Exercise:
Moderate exercise during the day can improve sleep quality and duration, but intense activity should be avoided close to bedtime.
Nighttime Routines for Glowing Skin
In addition to promoting better sleep quality, a consistent nighttime skincare routine can enhance the skin’s natural repair processes.
- Cleansing:
Remove makeup, sunscreen, and impurities to prevent clogged pores and allow skin to breathe during sleep. - Exfoliation (2–3 times per week):
Gentle exfoliation removes dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover and absorption of active ingredients. Avoid harsh scrubs close to bedtime to prevent irritation. - Serums and Treatments:
Apply targeted treatments containing antioxidants, peptides, or retinoids to support collagen production and repair cellular damage. - Moisturization:
Night creams or moisturizers replenish hydration lost during the day and reinforce the skin barrier. Look for products with hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or nourishing oils. - Eye Care:
Use eye creams or gels containing peptides, caffeine, or hyaluronic acid to address under-eye puffiness and dark circles. - Sleep Position and Bedding:
Sleeping on your back reduces the risk of sleep lines and creases caused by pressing the face against the pillow. Use a clean, soft pillowcase, ideally silk or satin, to minimize friction.
The Role of Circadian Rhythm in Skin Health
The skin has its own circadian rhythm, with distinct day and night cycles:
- Daytime: Skin focuses on protection against UV damage, pollution, and pathogens. It produces antioxidants to combat free radicals.
- Nighttime: Skin shifts to repair and regeneration, increasing cell proliferation, protein synthesis, and barrier restoration.
Aligning sleep schedules with this natural rhythm maximizes the skin’s regenerative capacity, making regular, uninterrupted sleep critical for overall skin health.
Integrating Sleep and Skincare for Optimal Results
Combining proper sleep hygiene with an effective nighttime skincare routine amplifies results. For example:
- Getting 7–9 hours of quality sleep while using a collagen-stimulating serum enhances elasticity and reduces fine lines.
- Adequate sleep improves skin hydration, making moisturizers and humectants more effective.
- Managing stress through sleep reduces cortisol levels, which helps prevent acne flare-ups and inflammation.
By prioritizing sleep alongside a thoughtful skincare routine, individuals can achieve brighter, firmer, and more resilient skin over time.
Conclusion
Sleep is a fundamental pillar of skin health, influencing collagen production, elasticity, hydration, and the skin’s ability to repair itself. Chronic sleep deprivation accelerates aging, exacerbates inflammatory conditions, and diminishes overall radiance. Prioritizing sleep hygiene—through consistent schedules, a restful environment, and avoidance of stimulants—along with a carefully designed nighttime skincare routine can dramatically enhance skin appearance. Ultimately, glowing, healthy skin is not just about products; it is the reflection of a body well-rested and supported by restorative sleep.