Sensitive skin can be a tricky concern, often characterized by redness, irritation, dryness, and a heightened reaction to environmental changes or skincare products. When it comes to using active ingredients in skincare—like acids, retinoids, and antioxidants—the question arises: Is it safe for sensitive skin to use products containing these potent ingredients? The answer depends on the individual’s skin type, the specific active ingredients, and how they are incorporated into your routine.
In this article, we’ll explore how sensitive skin reacts to active ingredients, which actives are safe (and which are best avoided), and how to use them correctly for effective skincare without causing irritation.
What Is Sensitive Skin?
Sensitive skin refers to skin that is prone to irritation, redness, burning, or stinging when exposed to certain substances. These reactions can be triggered by environmental factors, such as changes in temperature or humidity, or by the use of harsh skincare products. Common signs of sensitive skin include:
- Redness or flushing
- Dryness or tightness
- Itchiness or stinging sensations
- Rash or hives
- Reaction to cosmetics or skincare products
Sensitive skin may be genetic, or it can develop due to external factors like stress, pollution, or overuse of harsh products. It is also often linked with conditions like rosacea, eczema, and allergic contact dermatitis.
What Are Active Ingredients in Skincare?
Active ingredients are the key components of skincare formulations that are designed to target specific skin concerns, such as acne, pigmentation, or fine lines. These ingredients have scientifically proven effects and work by penetrating the skin’s surface to produce a visible change.
Some common types of active ingredients include:
- Exfoliants (AHAs, BHAs): These acids, such as glycolic acid (AHA) and salicylic acid (BHA), help to exfoliate the skin, clear pores, and smooth texture.
- Retinoids (Vitamin A): Retinoids, like retinol, are commonly used to treat acne, wrinkles, and fine lines.
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid): An antioxidant that brightens the skin and reduces signs of aging.
- Niacinamide: A form of Vitamin B3 that helps to reduce inflammation, redness, and hyperpigmentation.
- Peptides: Small proteins that help stimulate collagen production and strengthen the skin’s barrier.
- Hyaluronic Acid: A powerful humectant that draws moisture into the skin, helping to keep it hydrated.
While these ingredients can be highly effective, they can also cause irritation if not used correctly, especially for those with sensitive skin. The challenge lies in finding the right balance between reaping the benefits of these actives and avoiding irritation or adverse reactions.
Which Active Ingredients Are Safe for Sensitive Skin?
Sensitive skin can tolerate certain active ingredients more easily than others. The key is to choose the right ones and use them in a way that minimizes the risk of irritation. Here’s a breakdown of the most common active ingredients and how they affect sensitive skin:
1. Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
Why It’s Safe for Sensitive Skin:
- Niacinamide is one of the most well-tolerated ingredients for sensitive skin types. It has anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe and calm the skin.
- It also strengthens the skin’s natural barrier, which is crucial for sensitive skin, preventing moisture loss and protecting against external irritants.
- Niacinamide can help reduce redness and improve the appearance of uneven skin tone, making it an ideal choice for those with rosacea or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
How to Use:
- Niacinamide can be used twice daily. Look for serums or moisturizers that contain 5% or less of niacinamide to avoid irritation.
- If you’re new to niacinamide, start with a lower concentration and gradually increase as your skin builds tolerance.
2. Hyaluronic Acid
Why It’s Safe for Sensitive Skin:
- Hyaluronic acid is a gentle, hydrating ingredient that draws moisture into the skin without causing irritation. It is naturally present in the skin, so it is unlikely to trigger an allergic reaction.
- It’s ideal for those with sensitive or dry skin, as it provides a plump, dewy look while maintaining hydration.
How to Use:
- Apply hyaluronic acid serums to damp skin to help lock in moisture.
- It can be used daily, both in the morning and at night, without causing irritation.
3. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Why It’s Safe for Sensitive Skin (If Used Correctly):
- Vitamin C has antioxidant properties that protect the skin from free radical damage, brighten dull skin, and reduce pigmentation. However, ascorbic acid (pure Vitamin C) can be harsh for sensitive skin due to its acidic nature.
- To avoid irritation, sensitive skin types should opt for less potent forms of Vitamin C like ascorbyl glucoside or sodium ascorbyl phosphate, which are gentler but still offer skin-brightening benefits.
How to Use:
- Start with a Vitamin C serum with a low concentration (around 10% or less).
- Always apply it in the morning after your cleanser and before sunscreen.
- If irritation occurs, reduce frequency or switch to a gentler derivative of Vitamin C.
4. Peptides
Why It’s Safe for Sensitive Skin:
- Peptides are small chains of amino acids that help to stimulate collagen production and repair the skin’s barrier. They are generally well-tolerated by sensitive skin, making them an excellent choice for those looking for anti-aging benefits without irritation.
- Peptides help to strengthen and support the skin’s structure, reducing the risk of damage from environmental stressors.
How to Use:
- Peptide-based serums or moisturizers can be used daily.
- Layer peptides under your sunscreen and moisturizer in the morning or as part of your nighttime routine.
5. Chamomile and Aloe Vera
Why It’s Safe for Sensitive Skin:
- These natural ingredients are well-known for their soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. They can calm skin irritation, reduce redness, and provide relief to sensitive skin.
- Chamomile has antioxidant properties, while aloe vera helps to hydrate and heal the skin, making both of these ingredients great for sensitive skin that needs gentle care.
How to Use:
- Choose products that contain chamomile or aloe vera as part of their formulation, such as gentle cleansers or soothing masks.
- These can be used daily without risk of irritation.
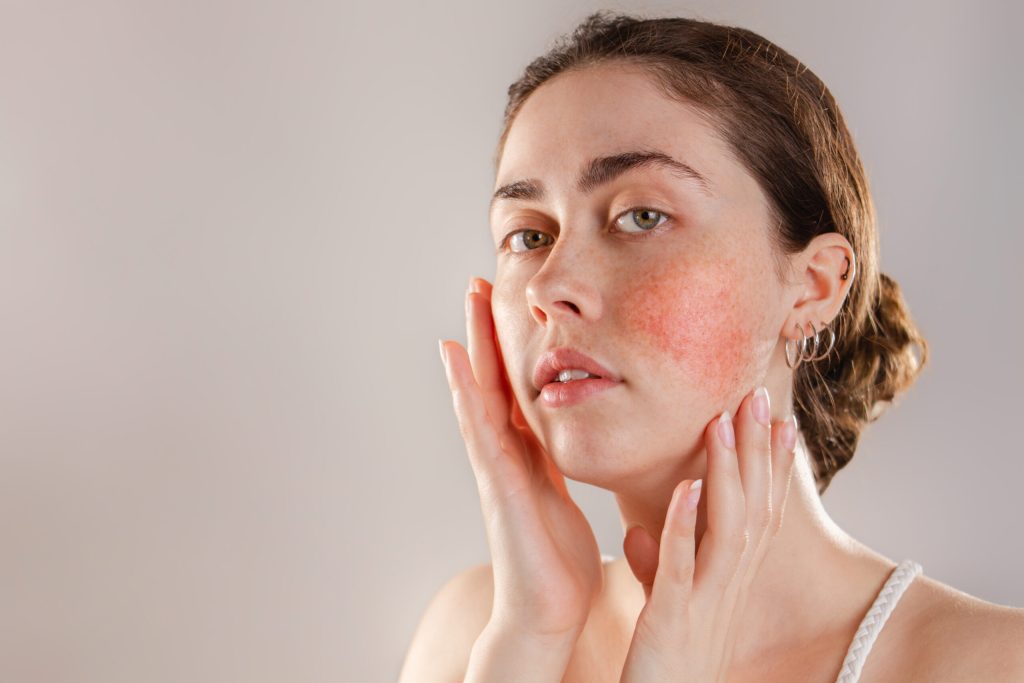

Which Active Ingredients Should Be Avoided for Sensitive Skin?
While some active ingredients are gentle enough for sensitive skin, others may cause irritation, burning sensations, or allergic reactions. Here’s a list of commonly used active ingredients that sensitive skin types should approach with caution or avoid altogether:
1. Retinoids (Retinol and Retinoid Derivatives)
Why It May Cause Issues:
- Retinoids, including retinol and tretinoin, are incredibly effective for reducing acne and fine lines, but they are known to cause dryness, redness, and peeling, especially when introduced too quickly or used in high concentrations.
- Sensitive skin can react with irritation, stinging, and increased sensitivity to the sun.
What to Do Instead:
- Consider using bakuchiol, a plant-based alternative to retinol, which offers similar benefits without the irritation.
- If you still want to use retinol, start with a lower concentration (0.25-0.5%) and apply it sparingly, only 2-3 times a week, and gradually build tolerance.
2. Strong Chemical Exfoliants (AHAs and BHAs)
Why They May Cause Issues:
- Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) are effective exfoliants that remove dead skin cells, but they can be too strong for sensitive skin.
- Products containing high concentrations of glycolic acid, lactic acid, or salicylic acid can increase redness, dryness, and irritation when overused.
What to Do Instead:
- Opt for gentler exfoliating acids like mandelic acid or lactic acid at lower concentrations (1-5%).
- Reduce exfoliation frequency and monitor how your skin responds, aiming for no more than 1-2 times per week.
3. Fragrances and Artificial Colorants
Why They May Cause Issues:
- Many skincare products, particularly those marketed as luxurious or “fragrant,” contain added fragrances or colorants, which are common irritants for sensitive skin.
- Fragrances can trigger allergic reactions, stinging, or even exacerbate conditions like eczema or rosacea.
What to Do Instead:
- Always choose fragrance-free products or those with naturally derived scents (e.g., essential oils) in small concentrations.
- Opt for hypoallergenic formulations whenever possible.
Tips for Using Active Ingredients on Sensitive Skin
- Start Slow: Introduce one active ingredient at a time into your routine. Start with a low concentration and gradually increase the frequency and potency as your skin builds tolerance.
- Patch Test: Always do a patch test before introducing a new active ingredient. Apply a small amount to a discreet area (like behind the ear or on your jawline) and wait 24-48 hours to see if any irritation develops.
- Hydration Is Key: Use a good moisturizer to maintain the skin’s barrier function, especially when using actives. Hydrated skin is less likely to experience irritation.
- Use Sunscreen: Many active ingredients, particularly acids and retinoids, can make your skin more sensitive to UV rays. Always wear broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher when using actives.
Conclusion: Can Sensitive Skin Use Active Ingredients?
Yes, sensitive skin can use active ingredients—but the key lies in choosing the right ones, using them in moderation, and following best practices to avoid irritation. Niacinamide, hyaluronic acid, peptides, and certain vitamin C derivatives can offer significant benefits without the risk of discomfort or damage. However, it’s important to approach more potent actives, like retinoids and strong exfoliants, with caution and always prioritize hydration and sun protection.
By paying attention to your skin’s needs and responses, you can incorporate effective active ingredients into your routine without compromising the health of your sensitive skin.