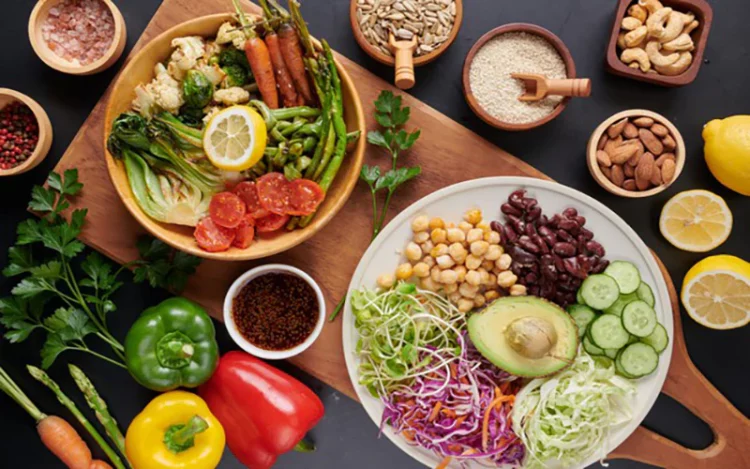
Maintaining a strong immune system and sustained energy levels is essential for overall health, disease prevention, and daily performance. Nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting these functions by providing the body with the necessary vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and macronutrients it needs to operate efficiently.
A well-balanced diet not only fuels physical activity but also enhances the body’s ability to fight off infections, repair damaged tissues, and maintain cellular health. This article delves into how adopting healthy eating habits can significantly strengthen immunity and vitality, along with practical tips for incorporating these habits into daily life.
1. The Link Between Nutrition and Immune Function
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that protect the body from pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Proper nutrition supports this system by:
- Providing antioxidants that reduce oxidative stress and inflammation
- Supplying micronutrients crucial for immune cell production and function
- Maintaining gut health, where a large portion of the immune system resides
Poor dietary habits can impair immune response, increasing susceptibility to infections and prolonging recovery time.
2. Key Nutrients That Enhance Immunity and Energy
Certain vitamins, minerals, and compounds in foods have been extensively studied for their immune-boosting and energy-enhancing effects.
Vitamin C
- Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli
- Supports white blood cell function and antibody production
- Acts as a powerful antioxidant to protect immune cells
Vitamin D
- Sources include fatty fish, fortified dairy, and sun exposure
- Modulates immune response and reduces inflammation
- Deficiency linked to increased risk of infections
Zinc
- Present in meat, shellfish, legumes, seeds, and nuts
- Essential for the development and activation of immune cells
- Aids wound healing and reduces severity of colds
B Vitamins (B6, B12, Folate)
- Found in whole grains, meats, eggs, and leafy greens
- Crucial for energy metabolism and production of immune cells
- Help reduce fatigue and support nervous system function
Protein
- From lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts
- Provides amino acids for building antibodies and immune factors
- Supports muscle repair and sustained energy levels
Antioxidants and Phytochemicals
- Abundant in colorful fruits and vegetables such as berries, spinach, and kale
- Reduce inflammation and oxidative damage to cells
- Support overall immune resilience
3. How Healthy Eating Habits Promote Sustained Vitality
Beyond specific nutrients, overall eating patterns strongly influence how energized and resilient you feel daily.
Balanced Meals
- Combining carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats ensures steady blood sugar levels and prevents energy crashes
- Whole grains, vegetables, nuts, and lean proteins help maintain satiety and focus
Hydration
- Adequate water intake supports digestion, nutrient transport, and cellular function
- Dehydration can cause fatigue, headaches, and impair immune efficiency
Regular Meal Timing
- Eating at consistent intervals prevents energy dips and overeating
- Supports metabolic regulation and hormone balance
Limiting Processed Foods and Sugars
- Excess sugar intake suppresses immune cell activity and increases inflammation
- Processed foods often lack essential nutrients and add unhealthy fats
4. Foods to Include for Immune and Energy Support
Incorporate the following foods regularly to boost your immunity and vitality:
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits) for Vitamin C
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) for Omega-3s and Vitamin D
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale) for antioxidants and folate
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds) for zinc and healthy fats
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas) for protein and fiber
- Whole grains (quinoa, oats) for sustained energy release
- Yogurt and fermented foods (kimchi, kefir) for gut health and immune modulation
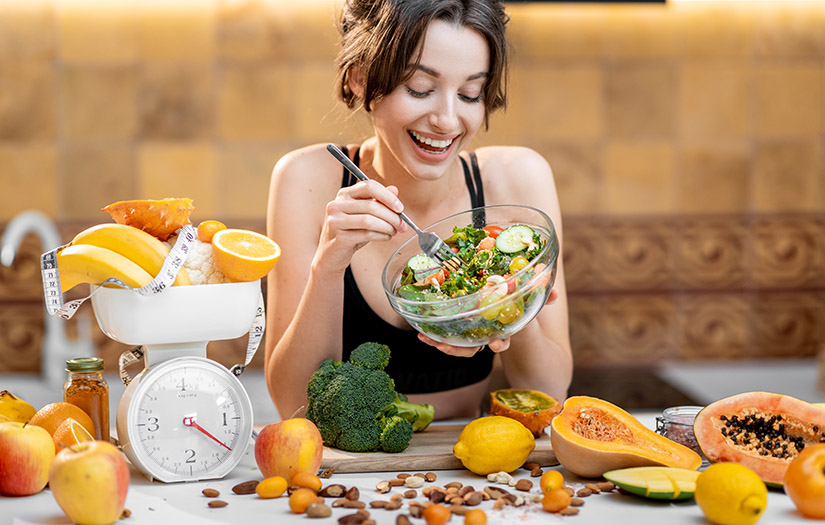

5. Practical Tips for Building Healthy Eating Habits
- Plan and prepare meals to avoid relying on fast or processed foods
- Snack smart with nuts, fruit, or yogurt instead of sugary snacks
- Stay hydrated by carrying a water bottle and drinking throughout the day
- Experiment with herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, and garlic known for their anti-inflammatory properties
- Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive intake weakens immune function
6. The Role of Gut Health in Immunity
Approximately 70% of the immune system is housed in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). A healthy gut microbiome enhances immune responses by:
- Supporting production of protective antibodies
- Training immune cells to distinguish harmful pathogens from harmless substances
- Reducing chronic inflammation
Eating probiotic-rich foods and prebiotic fibers promotes a diverse, balanced microbiome. Examples include:
- Fermented foods: yogurt, sauerkraut, kombucha
- High-fiber foods: onions, garlic, bananas, asparagus
7. Lifestyle Factors That Complement Healthy Eating
To maximize the immune-boosting benefits of nutrition, combine healthy eating with other lifestyle habits:
- Regular exercise enhances circulation and immune surveillance
- Adequate sleep allows recovery and hormone regulation
- Stress management through mindfulness or relaxation techniques prevents immune suppression
Conclusion
Healthy eating habits are foundational to building a robust immune system and sustaining high energy levels. By focusing on nutrient-dense whole foods, maintaining balanced meals, staying hydrated, and supporting gut health, you empower your body to defend itself effectively and keep you vibrant every day.
Adopting these dietary principles alongside positive lifestyle choices can help you maintain optimal vitality and resilience, reducing illness risk and enhancing overall well-being.