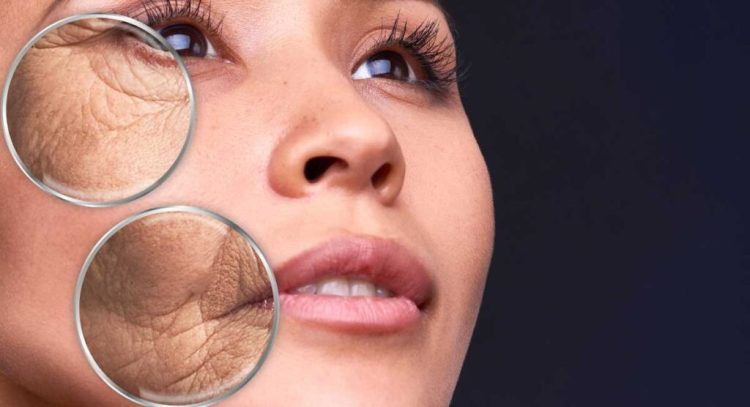
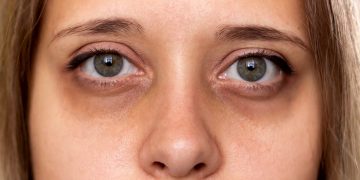
Maintaining healthy skin involves more than just topical creams and serums—it starts from within. One often-overlooked factor affecting skin health and aging is blood sugar regulation. Frequent spikes in blood glucose can trigger a cascade of biochemical reactions that compromise collagen, elastin, and overall skin integrity. This phenomenon, known as glycation, accelerates wrinkles, dullness, and loss of firmness, linking diet and lifestyle directly to premature aging.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore glycation, the role of sugar-heavy diets in skin aging, foods that help stabilize blood sugar, and daily habits that promote metabolic and skin health.
1. What Is Glycation and How Does It Affect Your Skin?
Glycation is a natural chemical process where excess glucose binds to proteins, forming advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These AGEs accumulate in tissues, including the skin, and have significant consequences for its structure and function.
A. Mechanism
- Glucose molecules attach to collagen and elastin fibers in the skin.
- Cross-linking of these proteins makes them stiff and brittle, reducing elasticity.
- Damaged collagen and elastin contribute to fine lines, sagging, and wrinkles.
B. Accelerated Aging
- Glycation disrupts the skin’s natural repair mechanisms.
- AGE accumulation increases oxidative stress, promoting inflammation and tissue damage.
- Over time, this process contributes to a loss of firmness, dullness, and uneven texture.
Key Insight: Glycation doesn’t just affect the skin’s appearance—it also impairs its structural integrity, making preventative lifestyle strategies crucial.
2. How Do Sugar-Heavy Diets Contribute to Wrinkles?
Frequent consumption of high-glycemic foods leads to rapid blood sugar spikes, which in turn accelerate glycation.
A. Common Culprits
- Sugary snacks, desserts, and sodas
- Refined carbohydrates like white bread, pastries, and pasta
- Sweetened beverages, including energy drinks and flavored coffees
B. Impact on Skin
- Glycation damages collagen and elastin, leading to loss of elasticity
- Increases inflammation, promoting redness, puffiness, and uneven tone
- Accelerates the formation of crow’s feet, laugh lines, and forehead wrinkles
C. Scientific Evidence
- Studies show that individuals with high sugar intake develop more pronounced skin aging than those with low-glycemic diets.
- Glycation markers are higher in aging skin exposed to frequent sugar spikes.
Bottom Line: Excessive sugar intake is a silent but powerful factor in premature skin aging, emphasizing the importance of diet in aesthetic longevity.
3. Which Foods Help Stabilize Blood Sugar and Protect Skin?
Eating strategically can reduce glycation, support collagen integrity, and promote healthier skin.
A. Low-Glycemic Carbohydrates
- Whole grains (quinoa, oats, brown rice)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans)
- Root vegetables (sweet potatoes, carrots)
B. Protein-Rich Foods
- Lean meats, poultry, fish
- Eggs and dairy products
- Plant-based proteins like tofu and tempeh
C. Healthy Fats
- Avocado, nuts, seeds
- Olive oil and fatty fish rich in omega-3s
- Fat slows glucose absorption, reducing blood sugar spikes
D. Fiber and Antioxidant-Rich Foods
- Leafy greens, berries, cruciferous vegetables
- Citrus fruits for vitamin C, which supports collagen synthesis
- Polyphenols in green tea and cocoa help combat glycation-induced oxidative stress
Practical Tip: Pairing carbohydrates with protein, fat, or fiber reduces rapid glucose surges and supports long-term skin health.

4. What Daily Habits Help Maintain Balanced Blood Sugar?
Lifestyle choices beyond diet are critical for glycemic control and overall skin wellness.
A. Regular Physical Activity
- Aerobic exercise improves insulin sensitivity
- Strength training helps regulate blood sugar and supports metabolism
- Even daily walks or short workouts reduce post-meal spikes
B. Mindful Eating
- Avoid overeating or eating late at night
- Eat slowly to allow proper digestion and prevent glucose surges
- Monitor portion sizes, especially of high-carb foods
C. Stress Management
- Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can raise blood sugar
- Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing improve hormonal balance and skin appearance
D. Adequate Sleep
- Sleep deprivation disrupts insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism
- Consistent 7–9 hours per night helps maintain balanced blood sugar and supports skin repair
E. Hydration
- Water helps transport nutrients, flush toxins, and maintain skin elasticity
- Proper hydration complements blood sugar stabilization efforts
Key Insight: Balanced lifestyle habits reinforce dietary strategies, creating a holistic approach to glycation prevention and anti-aging.
5. How Can You Integrate Glycation Awareness Into Your Skincare Routine?
While internal strategies are paramount, topical care can mitigate some of glycation’s visible effects.
A. Antioxidant Skincare
- Vitamin C, E, and ferulic acid protect collagen from oxidative stress induced by AGEs
- Apply serums in the morning under sunscreen for optimal effect
B. Collagen-Boosting Treatments
- Retinoids stimulate collagen production to counteract glycation damage
- Microneedling or light-based therapies can repair structural integrity over time
C. Sun Protection
- UV exposure accelerates glycation and collagen degradation
- Daily SPF 30+ shields skin from compounded damage
D. Anti-Inflammatory Topicals
- Niacinamide and peptides calm oxidative stress and support collagen synthesis
Combined Approach: Addressing glycation internally via diet and lifestyle, while supporting skin externally, provides the most effective anti-aging strategy.
6. Final Thoughts: Can Managing Blood Sugar Slow Skin Aging?
The connection between blood sugar and skin aging underscores the importance of a holistic approach to beauty and wellness. Frequent spikes in glucose accelerate glycation, damaging collagen and elastin, and leading to premature wrinkles, sagging, and dullness.
By:
- Choosing low-glycemic, nutrient-rich foods,
- Practicing regular exercise, stress management, and proper sleep,
- Supporting the skin externally with antioxidants, collagen stimulators, and sun protection,
individuals can significantly reduce glycation’s impact. Managing blood sugar isn’t just beneficial for overall health—it’s a powerful, science-backed strategy for maintaining youthful, resilient skin.
Understanding the interplay between diet, lifestyle, and skin physiology empowers informed choices that slow aging from within, complementing external skincare for lasting beauty and vitality.