The skin barrier, also known as the stratum corneum, is the body’s first line of defense against environmental aggressors, pathogens, and moisture loss. When this barrier is compromised, skin can become dry, irritated, sensitive, or prone to breakouts and inflammation. Understanding the signs of a damaged skin barrier, the ingredients that help restore it, daily habits that support barrier health, and avoiding harmful practices is crucial for maintaining healthy, resilient skin. This guide explores these topics in depth, providing practical strategies for repairing and protecting your skin barrier.
What Is the Skin Barrier?
The skin barrier is the outermost layer of the epidermis, composed of corneocytes (dead skin cells) embedded in a lipid matrix of ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Its primary functions include:
- Protecting Against External Irritants: Blocks bacteria, pollutants, and allergens.
- Retaining Moisture: Prevents transepidermal water loss (TEWL), keeping skin hydrated.
- Supporting Skin Health: Maintains pH balance and optimal function of enzymes and cells.
A healthy barrier is essential for overall skin resilience and appearance, while a compromised barrier can lead to chronic dryness, inflammation, and premature aging.
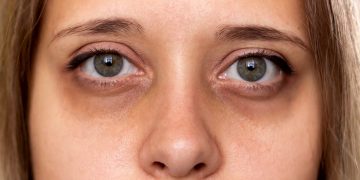
Signs of a Damaged Skin Barrier
Recognizing barrier damage early is crucial to prevent long-term skin issues. Common signs include:
- Dryness and Flakiness
- Skin may feel rough, tight, or dehydrated despite regular moisturizing.
- Flaky patches indicate that the lipid matrix is compromised.
- Redness and Sensitivity
- Irritation, stinging, or burning sensations, especially after applying skincare products.
- Skin may react to previously well-tolerated products.
- Breakouts and Inflammation
- Compromised barriers allow bacteria and pollutants to penetrate, triggering acne or eczema flare-ups.
- Increased Oiliness
- Paradoxically, the skin may overproduce sebum to compensate for moisture loss in damaged areas.
- Delayed Healing
- Cuts, scratches, or acne lesions take longer to recover due to impaired barrier function.
Ingredients to Restore the Skin Barrier
Restoring the skin barrier involves replenishing lipids, hydrating the skin, and reducing inflammation. Key ingredients include:
- Ceramides
- Essential lipids that rebuild the barrier’s protective structure.
- Often included in creams and serums designed for sensitive or dry skin.
- Cholesterol and Fatty Acids
- Work alongside ceramides to reinforce barrier integrity.
- Found in lipid-rich moisturizers and oils.
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Attracts and retains moisture, supporting skin hydration without irritation.
- Glycerin
- Humectant that draws water into the skin, keeping it soft and supple.
- Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
- Supports barrier repair, reduces inflammation, and improves skin elasticity.
- Squalane
- Lightweight oil that strengthens the barrier and locks in hydration.
- Panthenol (Vitamin B5) and Allantoin
- Soothing and repairing agents that calm irritation and promote healing.
Daily Habits to Support a Healthy Skin Barrier
In addition to using the right products, lifestyle and daily habits play a critical role in maintaining barrier function:
- Gentle Cleansing
- Avoid harsh soaps, foaming cleansers, or exfoliating too frequently.
- Use lukewarm water to prevent stripping natural oils.
- Moisturizing Consistently
- Apply barrier-repairing moisturizers morning and night to lock in hydration.
- Layer lighter serums under richer creams if needed.
- Sun Protection
- UV rays damage the barrier and accelerate moisture loss.
- Use broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
- Balanced Diet and Hydration
- Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and water support skin barrier integrity from within.
- Limit excessive sugar and processed foods that can increase inflammation.
- Stress Management
- Chronic stress can trigger inflammation and compromise barrier function.
- Incorporate relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or adequate sleep.

Avoiding Harmful Practices
Certain practices can damage the skin barrier or impede repair:
- Over-Exfoliation
- Excessive chemical or physical exfoliation removes protective lipids and irritates the skin.
- Limit exfoliation to 1–2 times per week with gentle products.
- Hot Showers or Baths
- High temperatures strip oils from the skin, increasing TEWL.
- Use lukewarm water instead.
- Harsh or Fragrant Products
- Alcohol, synthetic fragrances, and strong preservatives can irritate sensitive skin.
- Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic formulations.
- Skipping Moisturizer
- Neglecting hydration leads to persistent dryness and impaired barrier repair.
- Ignoring Skin Signals
- Redness, tightness, or itching are warnings that the barrier is compromised.
- Adjust routines and products promptly to prevent worsening conditions.
Repair Strategies for Compromised Skin
- Simplify Your Routine
- Reduce the number of products and focus on essentials: gentle cleanser, hydrating serum, and barrier-repairing moisturizer.
- Introduce Actives Gradually
- Potent ingredients like retinoids or acids can exacerbate barrier damage if introduced too quickly.
- Start with low concentrations and increase slowly while monitoring skin response.
- Patch-Test New Products
- Always test on a small area before applying broadly to avoid widespread irritation.
- Layer Hydration Strategically
- Apply humectants like hyaluronic acid on slightly damp skin, followed by occlusives or emollients to lock in moisture.
- Avoid Irritating Treatments Temporarily
- During barrier repair, minimize chemical peels, harsh exfoliants, and aggressive scrubs.
Final Thoughts
A healthy skin barrier is the cornerstone of resilient, radiant skin. Recognizing the signs of damage, using restorative ingredients, maintaining supportive daily habits, and avoiding harmful practices are all essential for repair and prevention. By focusing on hydration, gentle care, and protection, you can restore barrier function, reduce sensitivity, and improve overall skin health. With consistency, patience, and mindful product selection, your skin barrier can recover, leaving skin stronger, smoother, and better able to withstand environmental stressors.