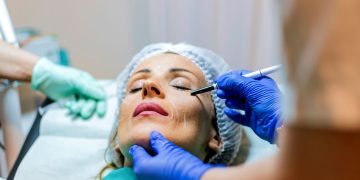
Facial aesthetics play a crucial role in an individual’s appearance and self-confidence. While many seek facial contouring or slimming procedures, others desire a fuller or larger facial appearance to achieve balance, symmetry, or cultural preferences. Facial enlargement via plastic surgery is a specialized process that involves enhancing the dimensions of the face while maintaining a natural and proportional look. This article explores various methods, their benefits, potential risks, and considerations to help individuals make informed decisions.
1. Understanding the Need for Facial Enlargement
a. Why Enlarge the Face?
People opt for facial enlargement for various reasons:
- Cultural Aesthetics: In some cultures, a fuller face signifies health, wealth, or attractiveness.
- Proportional Balance: Certain facial shapes or sizes may appear disproportionate to the body.
- Aging Concerns: Facial volume loss due to aging can make the face appear gaunt or hollow.
- Corrective Reasons: Addressing congenital conditions, trauma, or previous surgeries.
b. Who Are the Ideal Candidates?
Ideal candidates for facial enlargement surgery are:
- In good general health.
- Having realistic expectations about the outcomes.
- Free of severe skin or connective tissue disorders.
- Looking to address specific concerns about facial proportions or volume.
2. Methods for Facial Enlargement
Several surgical and non-surgical options exist to enlarge the face. Each technique offers unique benefits and is suitable for specific needs.
a. Facial Implants
Facial implants are a permanent solution to enhance specific areas of the face.
- Cheek Implants: Add volume and prominence to the mid-face, creating a fuller appearance.
- Jaw Implants: Enhance the jawline for a broader or more defined lower face.
- Chin Implants: Augment the chin to create balance with other facial features.
Procedure: Implants are typically made from silicone or other biocompatible materials and are inserted through incisions in the mouth or under the chin.
Benefits: Long-lasting, customizable shapes and sizes.
Risks: Infection, shifting of implants, or asymmetry.
b. Fat Grafting (Fat Transfer)
Fat grafting involves transferring fat from one part of the body to the face.
- Procedure: Liposuction is performed to harvest fat, which is then purified and injected into areas like the cheeks, temples, or jawline.
- Benefits: Natural-looking results, biocompatibility.
- Risks: Uneven fat absorption, need for multiple sessions.
c. Dermal Fillers
Non-surgical facial enlargement can be achieved with dermal fillers made of hyaluronic acid or other substances.
- Procedure: Fillers are injected into target areas to add volume and reshape the face.
- Benefits: Minimal downtime, immediate results.
- Risks: Temporary results, risk of overfilling or allergic reactions.
d. Bone Augmentation or Reshaping
For a more permanent solution, bone augmentation or reshaping techniques can be employed.
- Procedure: This involves adding bone grafts or prosthetics to areas like the jaw or cheeks.
- Benefits: Permanent changes.
- Risks: Extensive recovery time, higher risk of complications.
3. Choosing the Right Procedure
Selecting the appropriate procedure depends on several factors:
a. Goals and Expectations
Understanding the desired outcome is crucial. Consulting with a qualified plastic surgeon helps align expectations with achievable results.
b. Anatomy and Proportions
Each person’s facial structure is unique, and procedures should complement natural features.
c. Health and Lifestyle
Certain medical conditions or habits, like smoking, may influence the choice and success of a procedure.
d. Budget and Maintenance
Surgical options like implants or bone augmentation may involve higher costs upfront but have long-lasting results. Non-surgical options like fillers require regular maintenance.

4. Pre-Operative Considerations
Before undergoing facial enlargement surgery, consider the following:
a. Consultation
A thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon is essential. Discuss:
- Goals and expectations.
- Medical history and any allergies.
- Possible complications and risks.
b. Preparation
Patients may need to:
- Stop smoking or taking certain medications.
- Arrange for post-surgical care and recovery time.
c. Understanding Risks
While these procedures are generally safe, risks include:
- Swelling and bruising.
- Infection or allergic reactions.
- Dissatisfaction with results.
5. Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Proper care after surgery is vital for achieving optimal results:
a. Immediate Recovery
- Expect swelling and bruising, which typically subside within weeks.
- Follow all care instructions provided by the surgeon.
b. Long-Term Maintenance
- Regular follow-ups to monitor progress.
- Non-surgical touch-ups if necessary.
6. Real-Life Success Stories
Many individuals who undergo facial enlargement procedures report increased self-confidence and satisfaction. Sharing case studies or testimonials can provide insight into the transformative potential of these surgeries.
7. Ethical and Psychological Considerations
a. Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD)
Patients with unrealistic expectations or BDD may not be suitable candidates.
b. Cultural and Social Impacts
Discussing how societal standards influence beauty ideals is crucial in understanding motivations.
8. Conclusion
Facial enlargement through plastic surgery offers a variety of solutions tailored to individual needs. Whether through implants, fat grafting, fillers, or bone augmentation, these procedures can create a fuller, more balanced appearance. However, making an informed decision requires careful consideration of goals, risks, and the expertise of the chosen surgeon. For those prepared to embark on this journey, the results can be life-changing, enhancing not just physical appearance but overall confidence and well-being.