Introduction
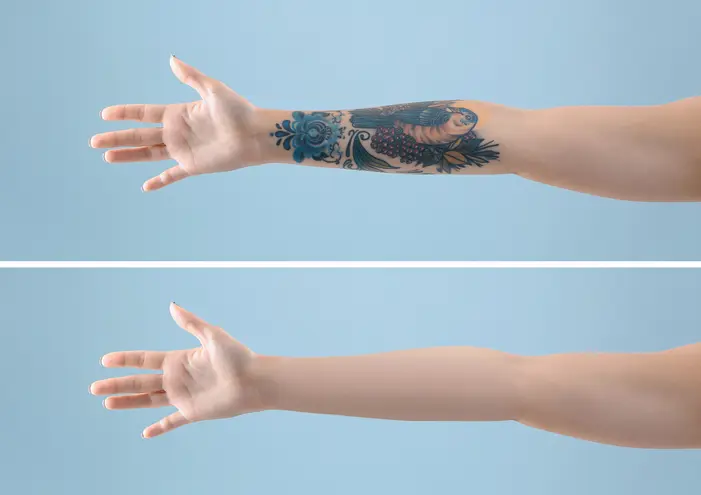
Tattoos have become a prominent form of personal expression, culture, and art, with millions of people worldwide opting to decorate their bodies with designs that reflect their identity, experiences, and creativity. However, over time, tastes and preferences can change, leading some individuals to seek tattoo removal. Whether due to regret, changing lifestyles, or professional requirements, tattoo removal has become a popular cosmetic procedure.
While tattoos are intended to be permanent, advancements in dermatology and laser technology have made tattoo removal increasingly effective and accessible. This article will explore the different methods of tattoo removal, the factors that influence success rates, potential risks and side effects, and what individuals can expect during the tattoo removal process.
Part 1: Why People Choose Tattoo Removal
1.1 Changing Preferences and Personal Growth
One of the most common reasons people seek tattoo removal is that their personal tastes and preferences change over time. A design that once held significant meaning may no longer resonate with an individual. For example, tattoos that were associated with a former partner, a past belief, or a specific phase in life may no longer align with a person’s current identity.
- Regret: Some people may experience regret after getting a tattoo, especially if they rushed into the decision or did not fully consider the long-term implications. As a result, they may feel that the tattoo no longer represents who they are or what they believe.
- Life Changes: Life events, such as a career change, marriage, or religious conversion, may prompt a desire to remove tattoos. Certain professions, such as law enforcement, healthcare, or corporate industries, may have policies that discourage visible tattoos, leading individuals to seek removal for professional reasons.
1.2 Social and Cultural Changes
Tattoos can carry different meanings in different cultural and social contexts. In some cultures, tattoos are celebrated, while in others, they may be viewed as inappropriate or unprofessional. As societal views on tattoos evolve, people may seek removal to align themselves with changing cultural norms.
- Stigma: In some areas or among specific social circles, tattoos may be associated with rebellion, non-conformity, or criminal behavior. Individuals may choose to remove their tattoos if they feel that the designs no longer fit with their lifestyle or social image.
1.3 Health Reasons
Though rare, some tattoos may cause health concerns, including allergic reactions to tattoo ink, infections, or skin sensitivities. For people who experience allergic reactions to specific ink colors or chemicals used in tattoos, removal may be necessary to avoid further complications.
- Ink Allergies: Certain pigments, such as red or yellow ink, can trigger allergic reactions, leading to rashes, swelling, or other skin issues. If these reactions persist, it may be necessary to have the tattoo removed.
- Infections: An improperly executed tattoo, poor aftercare, or exposure to unsanitary conditions during the tattooing process can lead to infections. If an infection is severe or persistent, removal of the tattoo may be required.
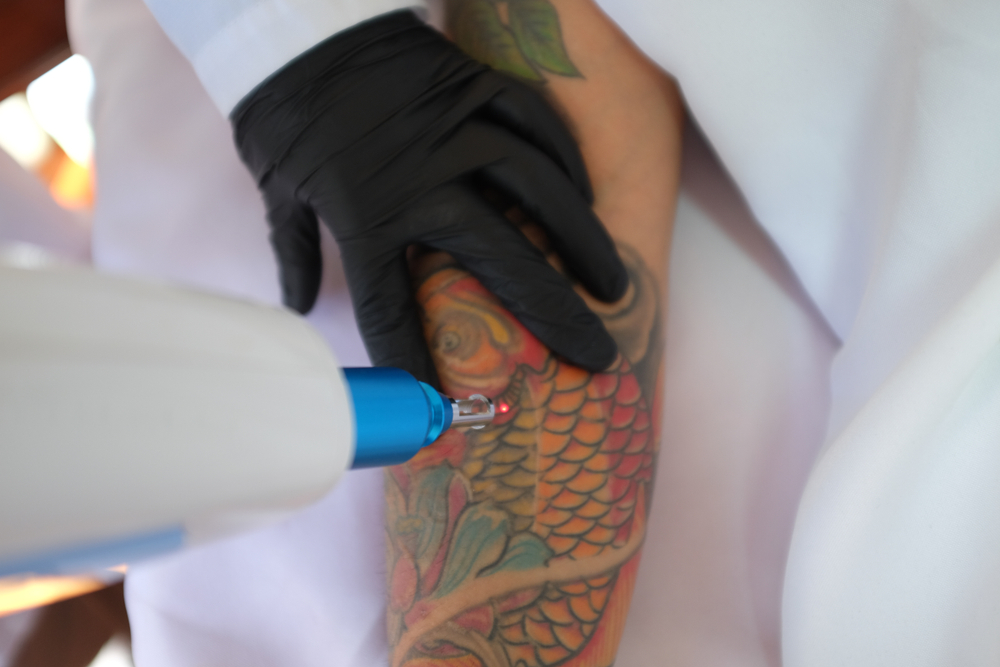
Part 2: Methods of Tattoo Removal
Over the years, various methods of tattoo removal have been developed. Some techniques are more effective than others, and the choice of method often depends on factors such as the type of tattoo, skin type, size of the tattoo, and individual preferences. Below, we explore the most commonly used methods for tattoo removal.
2.1 Laser Tattoo Removal
Laser tattoo removal is the most popular and widely practiced method of tattoo removal due to its effectiveness and relatively low risk of scarring. It works by using high-intensity laser light to break up the ink particles in the skin, which are then gradually absorbed by the body’s immune system.
- How It Works: The laser emits short pulses of light at specific wavelengths that target the tattoo pigment without harming surrounding skin tissue. The laser energy breaks the ink particles into smaller fragments, which are then cleared away by the body’s immune cells (macrophages).
- Types of Lasers:
- Q-Switched Lasers: These lasers are the most commonly used for tattoo removal. They release high-intensity light in a very short burst, making them effective at breaking down ink particles.
- Picosecond Lasers: A newer, more advanced type of laser that emits light in even shorter bursts than Q-switched lasers. Picosecond lasers are considered to be more effective at treating stubborn or multicolored tattoos.
- Laser Removal Process:
- Sessions: Multiple sessions are usually required to remove a tattoo completely, with each session spaced several weeks apart to allow the skin to heal and the immune system to process the broken-down ink.
- Pain and Comfort: Most patients report mild discomfort during laser removal, often described as a sensation similar to the snap of a rubber band on the skin. Topical numbing creams and cooling devices can be used to reduce discomfort.
- Effectiveness: Laser removal is highly effective for many tattoos, especially those with dark ink. Lighter inks (such as yellow or green) may be more difficult to treat and may require more sessions for full removal.
2.2 Surgical Tattoo Removal (Excision)
Surgical excision involves physically cutting out the tattooed skin and stitching the area back together. This method is typically used for small tattoos or tattoos in areas where other removal methods might be less effective.
- How It Works: A surgeon or dermatologist will remove the tattooed area of skin with a scalpel, and then close the wound with stitches. This method is most appropriate for small tattoos that are not suitable for laser treatment, as it removes the ink along with the skin in which the ink resides.
- Pros:
- Complete Removal: Surgical excision offers the potential for complete removal of small tattoos in one session.
- One-time Procedure: Unlike laser removal, which requires multiple sessions, excision typically takes place in a single procedure.
- Cons:
- Scarring: One of the main drawbacks of surgical tattoo removal is that it can result in scarring, especially if the tattooed area is large. Larger tattoos may require skin grafts, further increasing the risk of scarring.
- Limited Application: This method is not suitable for large tattoos or those in sensitive areas, such as the face.
2.3 Dermabrasion and Microdermabrasion
Dermabrasion and microdermabrasion are physical exfoliation methods that remove the top layers of skin. Dermabrasion involves using a rotating device to sand the skin’s surface, while microdermabrasion uses fine crystals to exfoliate the skin.
- How It Works: Dermabrasion works by physically “sanding” the tattooed skin, removing layers of skin to reveal fresh, untattooed tissue. Microdermabrasion is less invasive and more superficial, making it more suitable for surface-level tattoos or fading tattoos that are already partially removed.
- Effectiveness: These methods are less effective for full tattoo removal and are typically used for smaller tattoos or when the tattoo ink is not deeply embedded in the skin.
- Risks: Dermabrasion can cause significant discomfort and may lead to scarring, especially for tattoos that are deeply inked. Additionally, it is less effective for colorful tattoos compared to laser removal.
2.4 Tattoo Removal Creams
Tattoo removal creams are marketed as a non-invasive alternative to professional removal methods. These creams claim to gradually fade tattoos by breaking down the pigment in the skin over time.
- How They Work: Most tattoo removal creams contain ingredients such as hydroquinone, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), or other chemicals that claim to lighten the skin and gradually fade tattoos.
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of tattoo removal creams is highly debated, with many dermatologists and professionals in the field expressing skepticism. In general, tattoo removal creams are unlikely to fully remove a tattoo and can cause skin irritation, scarring, or damage.
- Risks: Prolonged use of tattoo removal creams can lead to skin damage, burns, or permanent scarring, especially if the ingredients are not used correctly. These products are not FDA-approved, and their safety and efficacy are not guaranteed.
Part 3: Factors Affecting Tattoo Removal Success
Several factors can influence the success of tattoo removal, including the method used, the tattoo itself, and the individual’s skin type. Understanding these factors can help set realistic expectations and determine the best approach for tattoo removal.
3.1 Tattoo Characteristics
- Ink Color: Darker inks, such as black and blue, are easier to remove with lasers, while lighter inks, such as yellow, green, and white, may be more resistant to laser treatment.
- Tattoo Size: Larger tattoos require more treatment sessions, making removal more time-consuming and costly.
- Tattoo Location: Tattoos on certain parts of the body, such as the arms or legs, may respond better to treatment than tattoos located in areas with poor circulation or more delicate skin, such as the face.
3.2 Skin Type and Health
- Skin Tone: People with darker skin may experience more challenges with laser removal, as the laser targets pigment. However, newer technologies, such as picosecond
lasers, have improved the effectiveness of treatment for darker skin types.
- Skin Sensitivity: Individuals with sensitive skin may experience more discomfort during the removal process and may have a higher risk of side effects such as hyperpigmentation, scarring, or infection.
3.3 Aftercare and Healing
Proper aftercare is critical for the success of tattoo removal. Individuals undergoing tattoo removal should follow all post-treatment instructions, which may include keeping the treated area clean, applying ointments, avoiding sun exposure, and refraining from scratching or picking at scabs.
Part 4: Risks and Side Effects of Tattoo Removal
While tattoo removal is generally safe, there are risks and side effects associated with the various methods. These risks can vary depending on the technique used, the skill of the practitioner, and the individual’s skin type.
- Laser Removal Risks: Side effects of laser removal can include temporary redness, swelling, blistering, scabbing, and changes in skin pigmentation (either hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation).
- Surgical Removal Risks: Risks associated with surgical excision include infection, scarring, and prolonged healing time.
- Dermabrasion Risks: Potential side effects include scarring, infection, and uneven skin texture, particularly with deep dermabrasion treatments.
Conclusion
Tattoo removal has become an increasingly viable option for those who regret their tattoos or wish to change their body art. With advances in technology, particularly laser removal techniques, the process has become safer and more effective than ever before. However, the choice of removal method should be carefully considered based on factors such as the tattoo’s size, color, location, and the individual’s skin type.
Ultimately, tattoo removal requires patience, multiple treatment sessions, and a commitment to proper aftercare to ensure the best possible results. By understanding the various methods, risks, and considerations involved in tattoo removal, individuals can make an informed decision about how to proceed with removing a tattoo that no longer fits their personal style or needs.